How to use variables with the Database Crawler
OpenSearchServer's database crawler's job is to crawl several types of database using an SQL query.
This SQL query can contain multiple variables, whose values will be set at execution time.
Defining variables in SQL queries
Variables can be used anywhere in a SQL query. They must be written using this format: {variableName}.
For example:
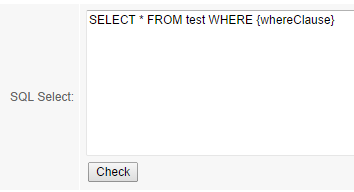
Giving variables some values
When using variables in SQL queries, they must be given a set value before using the Database Crawler. Otherwise, OpenSearchServer will use the variables names as given in the SQL query - resulting in a failure.
There are 2 ways to set variables.
Set variables using the REST API for the Database Crawler
To call this API and crawl a database, use:
- HTTP Method: PUT
- Header: Content-type:application/json
- URL:
.../services/rest/index/<index name>/crawler/database/<crawl name>/run?login=<login>&key=<API key>
Variables are defined along with the data for the request, using a JSON array:
{
"whereClause": "id=2"
}
Here is an example using the Postman extention for the Chrome browser :
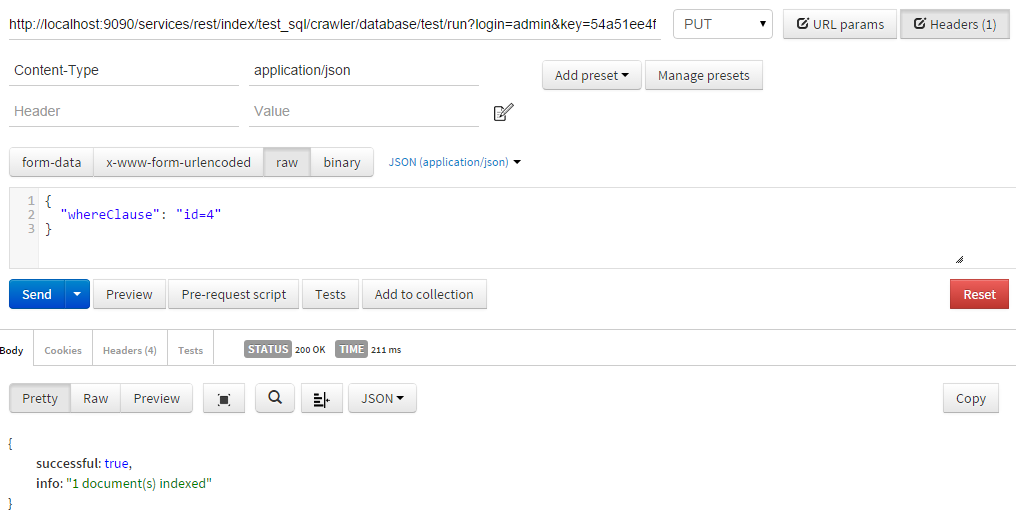
Set variables using Scheduler
OpenSearchServer's Scheduler can be used to run the Database Crawler. Use the task Database crawler - run to do this.
Variables have to be written, one by line, in the field crawl variables. Use the following format: variableName=replacement.
For example:
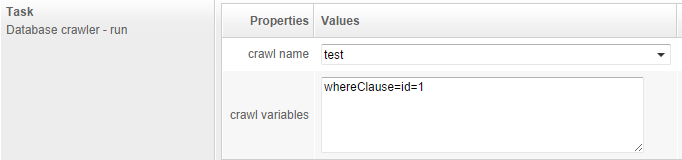
Running a scheduled job using the REST API
The Scheduler can be launched via an API call. The variables can be passed as a JSON array.
Here is an example using the Postman extention for the Chrome browser :
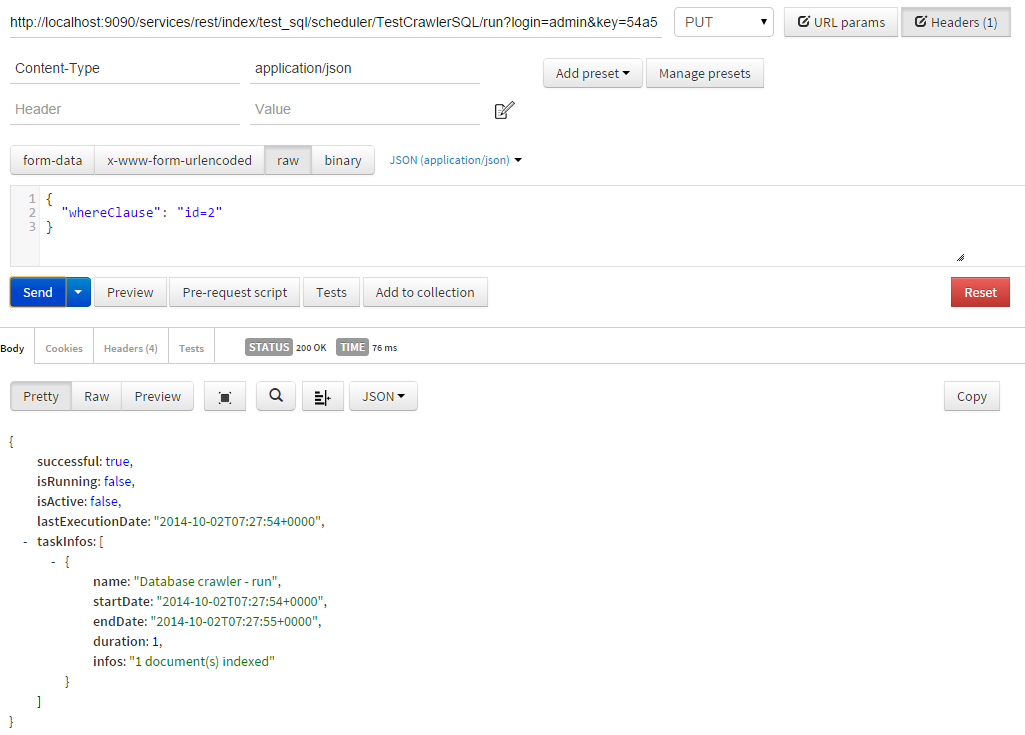
Giving variables an empty value
To set an empty value for a variable, pass an empty string.
For example, in JSON:
{
"whereClause": ""
}
Or in scheduler's task Database crawler - run:
whereClause=